Influence was imminent. Occasional gasps arose because the asteroid took form and a jagged, rocky floor crammed the view. Then the photographs abruptly stopped.
The mission control room at Johns Hopkins University Utilized Physics Lab in Laurel, Md., erupted in cheers. “We’ve affect!” mentioned the lead engineer, who gave a two-handed excessive 5 to a close-by colleague. Others waved their palms within the air in victory and slapped one another on the again.
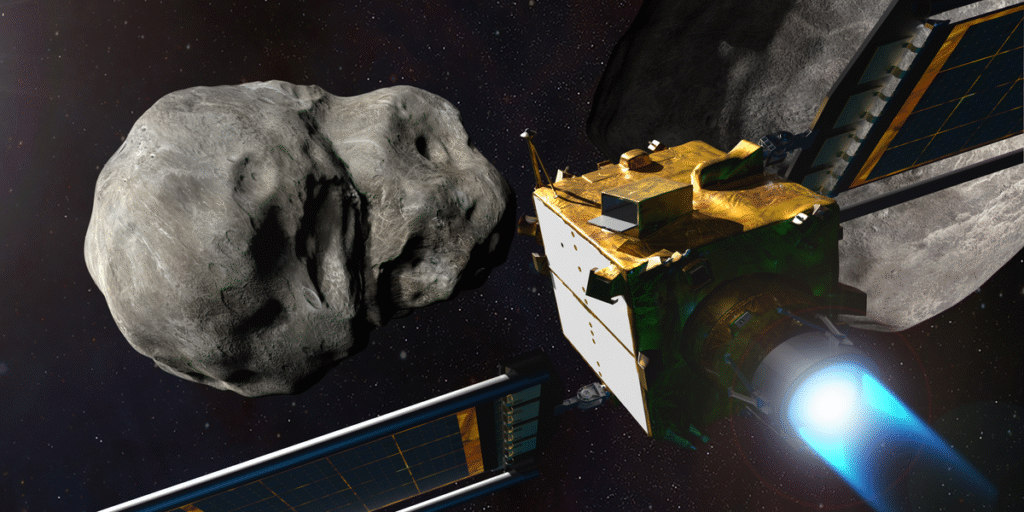
This had been a take a look at, and humanity had handed it, taking one essential step nearer to defending Earth from an asteroid affect. The test was the fruits of NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission, for which I used to be the coordination lead. On 26 September 2022, the DART spacecraft had efficiently crashed into Dimorphos, a roughly 150-meter-diameter asteroid that was 11 million kilometers from Earth. The collision nudged the asteroid and modified its trajectory.
In 2022, NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Check slammed a golf-cart-size spacecraft, DART, into the near-Earth asteroid Dimorphos (1). DART—which first deployed a small observer craft, LICIACube, to watch the collision (2)—bumped Dimorphos’s trajectory (3) sufficient to change its future course (4).GyGinfographics; Supply: NASA
The celebrations within the management room have been the fruits of years of effort to show that the momentum from a golf-cart-size spacecraft can alter an asteroid’s future path. And DART’s collision with asteroid Dimorphos kicked off a brand new period in space exploration, by which applied sciences for planetary protection are actually taking form.
If in the future an asteroid like Dimorphos is found to be headed towards Earth, an interceptor craft like DART might collide with the asteroid years prematurely to avert catastrophe. Right here’s how which may work.
Step 1: Discover and Observe Close to-Earth Asteroids
Step one in averting an asteroid affect with Earth is simply to know what near-Earth objects (NEOs) are on the market.
The College of Hawaii’s Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) station, in Chile performs a important function in these observations of NEOs, that are asteroids orbiting close to Earth’s orbit. In late December, it detected a beforehand unknown NEO throughout a routine sweep of the skies. The asteroid was given the identify 2024 YR4, following the standard astronomical convention for brand new objects. “2024 Y” represents the 24th-half-month of the year 2024—that’s, 16 to 31 December. The “R4” encodes the sequence of discovery—on this case, that it was the 117th object discovered throughout the yr’s closing couple of weeks.
Hera

Chris Philpot
This European Space Agency mission will rendezvous with the Didymos–Dimorphos asteroid system and examine the aftereffects of NASA’s DART affect shut up.
Launch:
2024
Rendezvous:
2026
Till that time within the yr, more than 3,000 NEOs had already been found. Nothing about 2024 YR4 initially stood out as regarding. It was a seemingly run-of-the-mill asteroid. Nonetheless, additional observations quickly urged it wasn’t unusual in any respect.
All through the primary weeks of 2025, the chance of a 2024 YR4 collision with Earth stored rising. On 29 January, astronomers calculated its odds of eventual affect to be 1.3 %. And in crossing the 1 % threshold, 2024 YR4 triggered an alert from the International Asteroid Warning Network to the United Nations’ Office for Outer Space Affairs in regards to the potential affect. Such alerts are posted publicly on the IAWN’s website. The 29 January notice assessed the areas of the planet at highest threat from 2024 YR4 (also referred to as its threat hall), in addition to the anticipated harm if the asteroid did crash into Earth.
On common, an object of 2024 YR4’s dimension—estimated at 60 meters throughout—slams into our planet as soon as each thousand years. It’s thought of a “city-killer” asteroid—not sufficiently big to set off a mass extinction, just like the estimated 10-km one which possible killed the dinosaurs, however nonetheless sufficiently big to be lethal as much as roughly 50 km from the affect location. Thankfully, by 24 February, further observations by telescopes throughout the globe had refined the asteroid’s trajectory sufficient to rule out near-term Earth affect.
But relating to asteroids and Earth, there gained’t at all times be such an uncomplicated, glad ending. One other asteroid that dimension and even bigger will ultimately be on a collision course with the planet [see chart below].

Amongst near-Earth object (NEO) asteroids, essentially the most devastating and least extensively catalogued classes right now are the 50-meter and 140-meter courses—also referred to as the “metropolis killers.”
The world’s area companies monitor an estimated 95 percent of NEOs greater than 1 km in diameter. The Worldwide Asteroid Warning Community and a associated Space Mission Planning Advisory Group (SMPAG) are world coordinating our bodies that monitor these efforts. And fortunately, not one of the big NEOs tracked by the above pose an affect threat to Earth for a minimum of the following hundred years. (In the meantime, comet impacts with Earth are even rarer than these of asteroids.)
However you may solely monitor the NEOs which might be identified. And loads of city-killer asteroids stay lurking and undiscovered, doubtlessly nonetheless posing an actual threat to life on the planet. Within the 50-meter vary, a meager 7 % of NEOs have been discovered. That’s not for lack of attempting. It’s simply tougher to seek out small asteroids as a result of smaller asteroids seem dimmer than bigger ones.
New {hardware} is clearly wanted. Someday quickly, the Vera C. Rubin Observatory, in Chile, is anticipated to see first gentle. The observatory will survey the complete seen sky each few nights, via a 3,200-megapixel digicam on an 8.4-meter telescope. No Earth-based telescope within the historical past of the NEO hunt can match its capabilities. Including to our NEO search will likely be NASA’s NEO Surveyor, an infrared space telescope scheduled to launch as quickly as 2027. Collectively, the 2 new services are anticipated to find 1000’s of new-to-us near-Earth asteroids. For objects 140 meters and bigger, the 2 telescopes will find an anticipated 90 % of the complete inhabitants.
As soon as an NEO has been found, astronomers routinely monitor its orbit and extrapolate its trajectory over the approaching century. So any NEO already on the books (for instance, in NASA’s database or ESA’s database) is sort of more likely to include a long time of warning. Ideally, that ought to go away ample time to develop and deploy a spacecraft to study extra about it and redirect the wayward area rock if mandatory.
Step 2: Ship an NEO Reconnaissance Mission
Think about that the chance of 2024 YR4 colliding with Earth rose as a substitute of fell, with the estimated affect to happen someday in 2032. Right here’s why that might have been particularly worrying.
Asteroid 2024 YR4’s elongated orbit made it unobservable from Earth after mid-Might of this yr. So we wouldn’t have been capable of see it with even essentially the most delicate telescopes till its subsequent swing via our area of the photo voltaic system—round June 2028.
In that alternate universe, we might’ve needed to wait three years to launch a reconnaissance mission to check the article up shut. Solely then would now we have identified the following steps to take to redirect the asteroid away from Earth earlier than its fated go to 4 years later.
Because it occurs, SMPAG held preliminary discussions about 2024 YR4 in late January and early February. Nonetheless, as a result of the asteroid’s threat of collision with Earth quickly dwindled to zero, the group didn’t develop particular suggestions.
Hayabusa2#

Chris Philpot
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Company has prolonged a earlier mission (Hayabusa2) to come across two extra near-Earth asteroids over the following six years.
Flyby:
2026
Rendezvous
2031
DART would have offered a basis for a 2028 reconnaissance mission, as would NASA’s Lucy mission, which flew previous the asteroid Dinkinesh in 2023. Reconnaissance flybys present as little as a number of valuable seconds to seize the wanted knowledge in regards to the goal asteroid. After all, inserting a reconnaissance craft into orbit across the asteroid would permit extra detailed measurements. Nonetheless, few NEO trajectories provide the chance for any maneuver aside from a flyby—particularly when time is of the essence.
Regardless of the trajectory, an important query for a reconnaissance mission can be whether or not the asteroid was the truth is on a collision course with Earth in 2032. If that’s the case, the place on the planet would it not hit? That future affect location might doubtlessly be narrowed down to within a hundred kilometers.
The mission may also uncover some issues. For starters, we’d uncover that the asteroid is definitely plural. Some 15 % of NEOs are believed to have secondary objects orbiting them—they’re asteroids with moons. And a few asteroids are primarily a flying jumble of rocks.
One other wrinkle is available in figuring out the asteroid’s mass. We have to know the mass to calculate the harm it might trigger on affect, in addition to the oomph required to divert it.
Sadly, the know-how to measure the mass of a city-killer asteroid doesn’t exist. The mass of a bigger, kilometer-size asteroid is measured by figuring out the gravitational pull on the reconnaissance spacecraft, however that trick doesn’t work for smaller asteroids. Proper now, the perfect we will do is estimate the mass by measuring the asteroid’s bodily dimension from closeup imaging throughout a flyby after which inferring the composition.
These challenges will should be mastered in time for the reconnaissance mission, because the spacecraft—touring at as much as 90,000 kilometers per hour—flies previous the possibly irregularly formed object or objects half-shrouded in darkness. So it most likely is sensible to deal with these challenges now quite than ready till an precise menace emerges.
Step 3: Change NEO’s Course With Interceptor
If the reconnaissance mission does conclude {that a} killer asteroid is on the best way and narrows down the date of affect, then what? Returning to 2024 YR4, which may make 22 December 2032 a really unhealthy day for one city-size area of the planet. Even when it fell within the ocean, we’d want to take a look at geological and oceanic computer models to forecast the tsunami threat. If that threat is small, then world leaders and NEO advisors may decide to let the asteroid proceed.
Alternatively, if the asteroid is heading in the right direction to strike a extremely populated space, then launching a spacecraft to deflect the asteroid and stop affect is perhaps warranted.
NEO Surveyor

Chris Philpot
NASA’s infrared area telescope has been designed to detect and monitor near-Earth object (NEO) asteroids which might be doubtlessly hazardous to Earth.
Launch:
as early as 2027
Right here, classes from DART are instructive. For one factor, a spacecraft affect can pack solely a lot punch. It’s unclear whether or not a deflection spacecraft the scale of the DART would be capable to nudge a 2024 YR4–like asteroid with sufficient drive to keep away from Earth. It’s additionally attainable the impactor’s nudge might inadvertently trigger it to land in an excellent worse spot, inflicting extra harm. And if the asteroid is simply weakly held collectively, a DART-like collision may break it into a number of, smaller rubble piles—a number of of which might nonetheless attain Earth. So any sort of deflection mission must be fastidiously thought of.
Different asteroid protection applied sciences are additionally price contemplating. These different choices are nonetheless untested, however we’d as properly get began, when nothing’s but at stake.
If in case you have a long time of lead time, as an illustration, a rendezvous spacecraft could possibly be dispatched to orbit the killer asteroid and slowly and frequently act on it. Researchers have urged using such a spacecraft’s gravity to tug the asteroid off its path or ion-beam engines to progressively push it. The spacecraft might use one or each strategies over the span of years or a long time to trigger a big sufficient change within the asteroid’s trajectory to forestall Earth affect.
But when time is brief, there are far fewer choices. If the state of affairs is dire sufficient, with a monster asteroid possible heading for a populated space, then utilizing a nuclear explosive to interrupt up or divert the asteroid could possibly be on the desk. That’s the premise of the 1998 blockbuster Armageddon (in addition to the 2021 Netflix satire Don’t Look Up). Absurd, sure, however price contemplating for those who’re in any other case out of choices.
After all, the entire concept of planetary protection is to have choices and to do as a lot advance preparation as attainable. Plenty of international locations have planetary-defense missions at the moment in area or deliberate within the subsequent few years.
The ESA’s Hera mission launched final yr and is on its technique to rendezvous late subsequent yr with the asteroid system that DART struck, to research the aftermath of DART’s 2022 deflection take a look at. The Japanese Aerospace Exploration Company’s Hayabusa2 is about to fly by an NEO in 2026 and rendezvous with a unique asteroid in 2031. It’s the following chapter to JAXA’s authentic Hayabusa2 mission, which introduced again samples of the asteroid Ryugu in 2020. China plans to perform a kinetic impactor demonstration just like DART, with an observer spacecraft to observe, scheduled to launch in 2027.
And in 2029, a 340-meter asteroid referred to as Apophis—after the Egyptian god of chaos and darkness—will move inside 32,000 km of Earth, which is nearer than some geosynchronous satellites. This may occur on 13 April 2029—Friday the thirteenth, that’s. Apophis gained’t hit Earth, however its shut move has prompted the U.N. to designate 2029 the International Year of Asteroid Awareness and Planetary Defense. The asteroid will likely be vivid sufficient to be seen by the bare eye throughout components of Europe, Asia, and Africa. And NASA has redirected its OSIRIS-REx spacecraft (which returned samples of the asteroid Bennu to Earth in 2023) to rendezvous with Apophis. The renamed OSIRIS-APEX mission will give astronomers an essential alternative to additional refine how we measure and characterize NEO asteroids.
Whereas NEO researchers will proceed to gather new knowledge and develop new insights and views, main towards, we hope, higher and stronger planetary protection, one perennial will maintain as true sooner or later because it does right now: On this very high-stakes recreation, you by no means get to select the asteroid. The asteroid at all times picks you.
From Your Website Articles
Associated Articles Across the Net