On 29 August 1949, the Soviet Union efficiently examined its first nuclear weapon. Over the following 12 months and a half, U.S. President Harry S. Truman resurrected the Workplace of Civilian Protection (which had been abolished on the finish of World Conflict II) and signed into regulation the Federal Civil Protection Act of 1950, which mobilized authorities companies to plan for the aftermath of a world nuclear conflict. With the Cold War underway, that act kicked off a decades-long effort to make sure that no less than some Individuals survived nuclear armageddon.
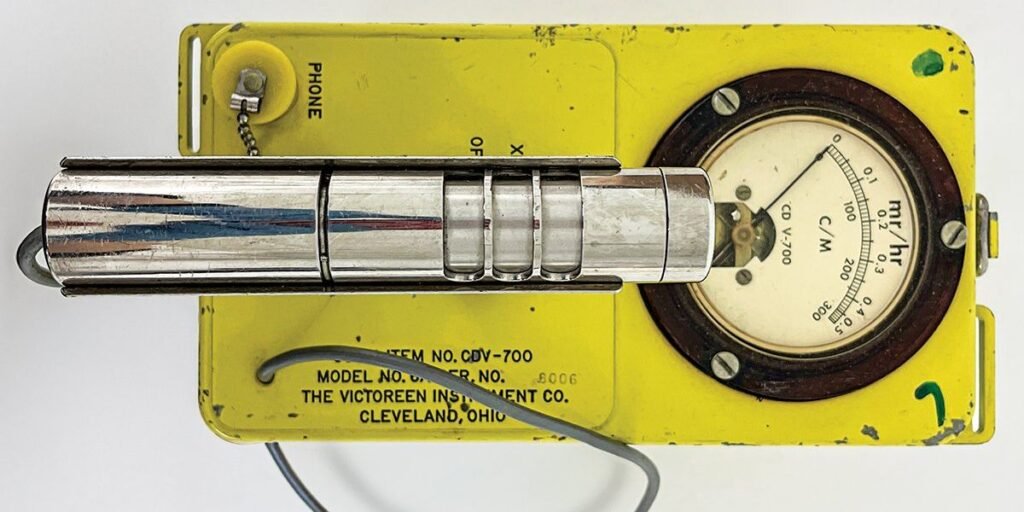
As the biggest civilian federal company with a presence all through the nation, the U.S. Put up Workplace Division was in a unique position to observe native radiation ranges and shelter residents. By the top of 1964, roughly 1,500 postal buildings had been designated as fallout shelters, offering house and emergency provides for 1.3 million individuals. Occupants have been anticipated to stay within the shelters till the radioactivity outdoors was deemed secure. By 1968, about 6,000 postal staff had been skilled to make use of radiological gear, such because the CD V-700 pictured at prime, to observe beta and gamma radiation. And a gaggle of postal staff organized a volunteer ham radio community to assist with communications ought to the common networks go down.
What was civil protection within the Chilly Conflict?
The essential premise of civil protection was that many individuals would die instantly in cities instantly focused by nuclear assaults. (Take a look at Alex Wellerstein’s interactive Nukemap for an estimate of casualties and affect ought to your hometown—or any location of your selecting—be hit.) It was the residents of different cities, suburbs, and rural communities outdoors the blast space that may most profit from civil protection preparations. With sufficient warning, they might shelter in a shielded website and look ahead to the worst of the fallout to decay. Anyplace from a day or two to some weeks after the assault, they might emerge and assist any survivors within the harder-hit areas.
In 1957, a committee of the Workplace of Protection Mobilization drafted the report Deterrence and Survival in the Nuclear Age, for President Dwight D. Eisenhower. Higher often called the Gaither Report, it referred to as for the creation of a nationwide community of fallout shelters to guard civilians. Authorities publications corresponding to The Family Fallout Shelter inspired Individuals who had the house, the sources, and the desire to assemble shelters for his or her properties. Metropolis dwellers in house buildings warranted solely half a web page within the booklet, with the suggestion to go to the basement and cooperate with different residents.
This mannequin fallout shelter from 1960 was designed for 4 to 6 individuals. Bettmann/Getty Photos
Finally, only a few householders truly constructed a fallout shelter. However Rod Serling, creator of the tv collection “The Twilight Zone,” noticed a possibility for pointed social commentary. Aired within the fall of 1961, the episode “The Shelter” confirmed how rapidly civilization (epitomized by a suburban middle-class household and their mates) broke down over selections about who could be saved and who wouldn’t.
In the meantime, President John F. Kennedy had began to shift the nationwide technique from particular person shelters to neighborhood shelters. At his instruction, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers started surveying present buildings appropriate for public shelters. Put up places of work, particularly ones with basements able to housing no less than 50 individuals, have been a pure match.
Every postmaster normal was designated because the native shelter supervisor and granted full authority to function the shelter, together with figuring out who could be admitted or excluded. The Handbook for Fallout Shelter Management gave steerage for all the pieces from sleeping preparations to sanitation requirements. Shelters have been stocked with meals and water, medication, and, after all, radiological survey devices.
What to do in case of a nuclear assault
These neighborhood fallout shelters have been issued a standard kit for radiation detection. The equipment got here in a cardboard field that contained two radiation displays, the CD V-700 (a Geiger counter, pictured at prime) and the CD V-715 (a easy ion chamber survey meter); two cigar-size CD V-742 dosimeters, to measure an individual’s complete publicity whereas carrying the system; and a charger for the dosimeters. Additionally included was the Handbook for Radiological Monitors, which offered directions on learn how to use the gear and report the outcomes.
 Put up workplace fallout shelters have been issued customary kits for measuring radioactivity after a nuclear assault.Nationwide Postal Museum/Smithsonian Establishment
Put up workplace fallout shelters have been issued customary kits for measuring radioactivity after a nuclear assault.Nationwide Postal Museum/Smithsonian Establishment
 The shelter radiation equipment included two radiation displays, two cigar-size dosimeters, and a charger for the dosimeters. Photoquest/Getty Photos
The shelter radiation equipment included two radiation displays, two cigar-size dosimeters, and a charger for the dosimeters. Photoquest/Getty Photos
Within the occasion of an assault, the operator would take readings with the CD V-715 at chosen places within the shelter. Then, inside three minutes of ending the indoor measurements, he would go outdoors and take a studying no less than 25 toes (7.6 meters) from the constructing. If the radiation stage outdoors was excessive, there have been procedures for decontamination upon returning to the shelter. The “safety issue” of the shelter was calculated by dividing the skin studying by the within studying. (At this time the Federal Emergency Administration Company, FEMA, recommends a PF of no less than 40 for a fallout shelter.) Operators have been directed to retake the measurements and recalculate the protecting issue no less than as soon as each 24 hours, or extra incessantly if the radiation ranges modified quickly.
The CD V-700 was supposed for detecting beta and gamma radiation throughout cleanup and decontamination operations, and likewise for detecting any radioactive contamination of meals, water, and personnel.
Every station would report their dose charges to a regional management heart, in order that the civil protection group might decide when individuals might go away their shelter, the place they might go, what routes to take, and what services wanted decontamination. However when you’ve lived by way of a pure or artifical catastrophe, you’ll know that within the instant aftermath, communications don’t at all times work so effectively. Certainly, the Handbook for Radiological Screens acknowledged {that a} nuclear assault would possibly disrupt communications. Fortunately, the U.S. Put up Workplace Division had a backup plan.
In Might 1958, Postmaster General Arthur E. Summerfield made an attraction to all postal staff who occurred to be licensed novice radio operators, to kind an off-the-cuff community that would offer emergency communications within the occasion of the collapse of phone and telegraph networks and industrial broadcasting. The outcome was Put up Workplace Web (PON), a voluntary group of ham radio operators; by 1962, about 1,500 postal staff in 43 states had signed on. That 12 months, PON was opened as much as nonemployees who had the mandatory license.
Though PON was by no means activated as a result of a nuclear menace, it did transmit messages throughout different emergencies. For instance, in January 1967, after an epic blizzard blanketed Illinois and Michigan with heavy snow, the Michigan PON went into motion, establishing liaisons with county climate companies and relaying emergency requests, corresponding to rescuing individuals stranded in autos on Interstate 94.
 A 1954 civil protection truthful featured a show of novice radios. The U.S. Put up Workplace recruited about 1,500 staff to function a ham radio community within the occasion that common communications went down. Nationwide Archives
A 1954 civil protection truthful featured a show of novice radios. The U.S. Put up Workplace recruited about 1,500 staff to function a ham radio community within the occasion that common communications went down. Nationwide Archives
The put up workplace retired the community on 30 June 1974 as a part of its shift away from civil protection preparedness. (A volunteer civil emergency-response ham radio network nonetheless exists, beneath the auspices of the American Radio Relay League.) And by 1977, laboratory exams indicated that a lot of the meals and medication stockpiled in put up workplace basements was now not fit to be eaten. In 1972 the Workplace of Civil Protection was changed by the Protection Civil Preparedness Company, which was finally folded into FEMA. And with the top of the Chilly Conflict, the civil protection program formally resulted in 1994, happily with out ever being wanted for a nuclear assault.
Will we nonetheless want civil protection?
The concept for this column got here to me final fall, once I was doing analysis on the Linda Hall Library, in Kansas Metropolis, Mo., and I saved coming throughout articles about civil protection in magazines and journals from the Nineteen Fifties and ’60s. I knew that the Smithsonian’s National Postal Museum, in Washington, D.C., had a number of civil protection artifacts (together with the CD V-700 and an awesome “In Time of Emergency” public service announcement document album).
As a baby of the late Chilly Conflict, I bear in mind being concerned by the prospect of nuclear conflict. However then the Chilly Conflict ended, and so did my fears. I envisioned this month’s column capturing the intriguing historical past of civil protection and the earnest preparations of the period. That chapter of historical past, I assumed, was closed.
Little did I think about that by the point I started to write down this, the prospect of a nuclear assault, if not an all-out conflict, would all of the sudden grow to be far more actual. Today, I perceive the complexities and nuances of nuclear weapons significantly better than once I was a baby. However I’m simply as involved {that a} nuclear battle is imminent. Right here’s hoping that historical past repeats itself, and it doesn’t come to that.
A part of a continuing series historic artifacts that embrace the boundless potential of know-how.
An abridged model of this text seems within the August 2025 print concern.
From Your Website Articles
Associated Articles Across the Internet