Hardly a day goes by with out spectacular new robotic platforms rising from educational labs and industrial startups worldwide. Humanoid robots specifically look more and more able to aiding us in factories and ultimately in properties and hospitals. But, for these machines to be actually helpful, they want refined ‘brains’ to manage their robotic our bodies. Historically, programming robots entails specialists spending numerous hours meticulously scripting advanced behaviors and exhaustively tuning parameters, similar to controller good points or motion planning weights, to attain desired efficiency. Whereas machine learning (ML) methods have promise, robots that have to be taught new advanced behaviors nonetheless require substantial human oversight and re-engineering. At Google DeepMind, we requested ourselves: how will we allow robots to be taught and adapt extra holistically and constantly, lowering the bottleneck of professional intervention for each vital enchancment or new talent?
This query has been a driving power behind our robotics analysis. We’re exploring paradigms the place two robotic brokers taking part in towards one another can obtain a larger diploma of autonomous self-improvement, transferring past programs which might be merely pre-programmed with fastened or narrowly adaptive ML fashions in the direction of brokers that may be taught a broad vary of expertise on the job. Constructing on our earlier work in ML with programs like AlphaGo and AlphaFold, we turned our consideration to the demanding sport of table tennis as a testbed.
We selected desk tennis exactly as a result of it encapsulates lots of the hardest challenges in robotics inside a constrained, but extremely dynamic, setting. Desk tennis requires a robotic to grasp a confluence of adverse expertise: past simply notion, it calls for exceptionally exact management to intercept the ball on the appropriate angle and velocity, and entails strategic decision-making to outmaneuver an opponent. These components make it a really perfect area for growing and evaluating sturdy studying algorithms that may deal with real-time interplay, advanced physics, excessive degree reasoning and the necessity for adaptive methods—capabilities which might be instantly transferable to functions like manufacturing and even doubtlessly unstructured dwelling settings.
The Self-Enchancment Problem
Commonplace machine studying approaches usually fall brief with regards to enabling steady, autonomous studying. Imitation studying, the place a robotic learns by mimicking an professional, sometimes requires us to supply huge numbers of human demonstrations for each talent or variation; this reliance on professional data collection turns into a big bottleneck if we wish the robotic to repeatedly be taught new duties or refine its efficiency over time. Equally, reinforcement learning, which trains brokers via trial-and-error guided by rewards or punishments, usually necessitates that human designers meticulously engineer advanced mathematical reward capabilities to exactly seize desired behaviors for multifaceted duties, after which adapt them because the robotic wants to enhance or be taught new expertise, limiting scalability. In essence, each of those well-established strategies historically contain substantial human involvement, particularly if the objective is for the robotic to repeatedly self-improve past its preliminary programming. Subsequently, we posed a direct problem to our crew: can robots be taught and improve their expertise with minimal or no human intervention in the course of the studying and enchancment loop?
Studying Via Competitors: Robotic vs. Robotic
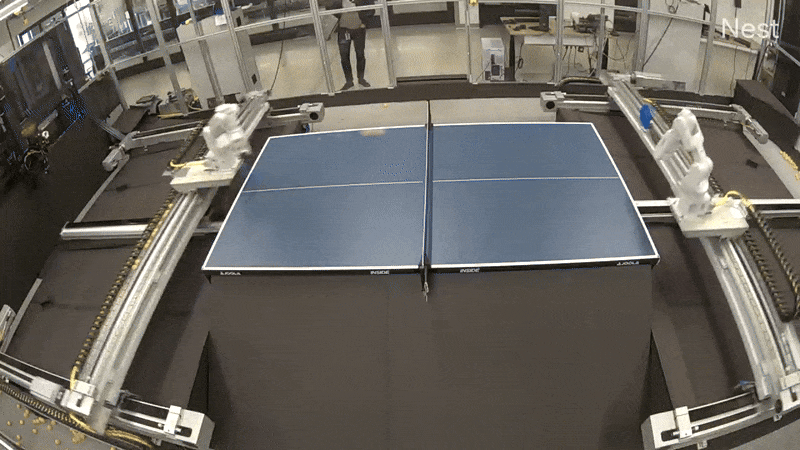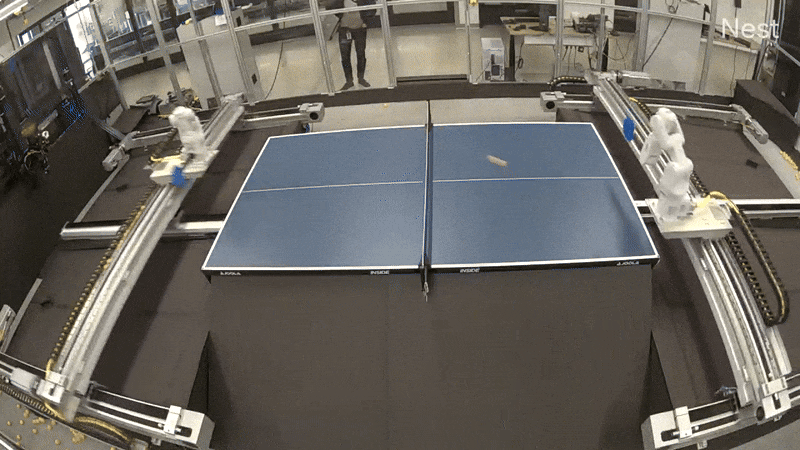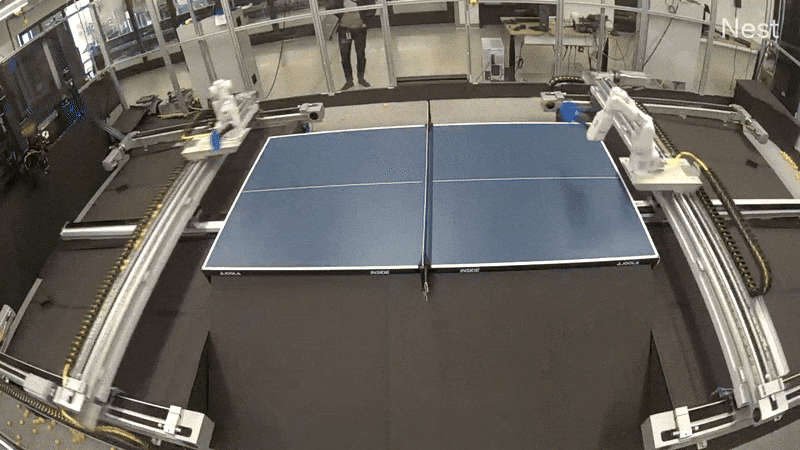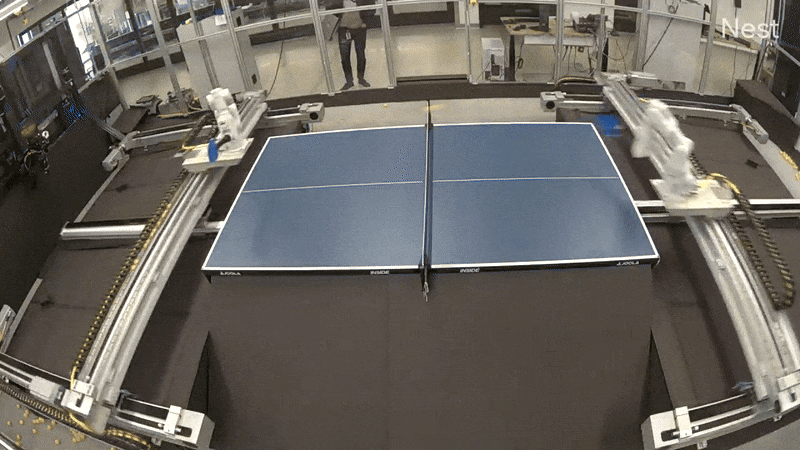
One revolutionary method we explored mirrors the technique used for AlphaGo: have brokers be taught by competing towards themselves. We experimented with having two robot arms play desk tennis towards one another, an thought that’s easy but highly effective: as one robotic discovers a greater technique, its opponent is pressured to adapt and enhance, making a cycle of escalating talent ranges.
To allow the intensive coaching wanted for these paradigms, we engineered a completely autonomous desk tennis setting. This setup allowed for steady operation, that includes automated ball assortment in addition to remote monitoring and management, permitting us to run experiments for prolonged intervals with out direct involvement. As a primary step, we efficiently skilled a robotic agent (replicated on each the robots independently) utilizing reinforcement studying in simulation to play cooperative rallies. We wonderful tuned the agent for a number of hours within the real-world robot-vs-robot setup, leading to a coverage able to holding lengthy rallies. We then switched to tackling the aggressive robot-vs-robot play.
Out of the field, the cooperative agent didn’t work effectively in aggressive play. This was anticipated, as a result of in cooperative play, rallies would settle right into a slender zone, limiting the distribution of balls the agent can hit again. Our speculation was that if we continued coaching with aggressive play, this distribution would slowly broaden as we rewarded every robotic for beating its opponent. Whereas promising, coaching programs via aggressive self-play in the true world offered vital hurdles—the rise in distribution turned out to be slightly drastic given the constraints of the restricted mannequin measurement. Basically, it was laborious for the mannequin to be taught to take care of the brand new photographs successfully with out forgetting previous photographs, and we rapidly hit a neighborhood minima within the coaching the place after a brief rally, one robotic would hit a straightforward winner, and the second robotic was not in a position to return it.
Whereas robot-on-robot aggressive play has remained a troublesome nut to crack, our crew additionally investigated how to play against humans competitively. Within the early phases of coaching, people did a greater job of conserving the ball in play, thus growing the distribution of photographs that the robotic may be taught from. We nonetheless needed to develop a coverage structure consisting of low degree controllers with their detailed talent descriptors and a excessive degree controller that chooses the low degree expertise, together with methods for enabling a zero-shot sim-to-real method to permit our system to adapt to unseen opponents in actual time. In a consumer research, whereas the robotic misplaced all of its matches towards probably the most superior gamers, it received all of its matches towards freshmen and about half of its matches towards intermediate gamers, demonstrating solidly beginner human-level efficiency. Outfitted with these improvements, plus a greater place to begin than cooperative play, we’re in an ideal place to return to robot-vs-robot aggressive coaching and proceed scaling quickly.
DeepMind
The AI Coach: VLMs Enter the Recreation
A second intriguing thought we investigated leverages the ability of Vision Language Models (VLMs), like Gemini. Might a VLM act as a coach, observing a robotic participant and offering steering for enchancment?
DeepMind
An essential perception of this undertaking is that VLMs could be leveraged for explainable robotic coverage search. Based mostly on this perception, we developed the SAS Prompt (Summarize, Analyze, Synthesize), a single immediate that permits iterative studying and adaptation of robotic conduct by leveraging the VLM’s capability to retrieve, motive and optimize to synthesize new conduct. Our method could be thought to be an early instance of a brand new household of explainable coverage search strategies which might be solely carried out inside an LLM. Additionally, there is no such thing as a reward perform—the VLM infers the reward instantly from the observations given the duty description. The VLM can thus develop into a coach that continuously analyses the efficiency of the scholar and offers strategies for tips on how to get higher.
 DeepMind
DeepMind
In the direction of Actually Realized Robotics: An Optimistic Outlook
Shifting past the restrictions of conventional programming and ML methods is crucial for the way forward for robotics. Strategies enabling autonomous self-improvement, like these we’re growing, cut back the reliance on painstaking human effort. Our desk tennis initiatives discover pathways towards robots that may purchase and refine advanced expertise extra autonomously. Whereas vital challenges persist—stabilizing robot-vs-robot studying and scaling VLM-based teaching are formidable duties—these approaches supply a novel alternative. We’re optimistic that continued analysis on this route will result in extra succesful, adaptable machines that may be taught the varied expertise wanted to function successfully and safely in our unstructured world. The journey is advanced, however the potential payoff of actually clever and useful robotic companions make it value pursuing.
The authors categorical their deepest appreciation to the Google DeepMind Robotics crew and specifically David B. D’Ambrosio, Saminda Abeyruwan, Laura Graesser, Atil Iscen, Alex Bewley and Krista Reymann for his or her invaluable contributions to the event and refinement of this work.
From Your Web site Articles
Associated Articles Across the Net